
ACT NO. 34 OF 2019 [9th August, 2019]
An Act to provide for the reorganisation of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir and for
matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
BE it enacted by Parliament in the Seventieth Year of the Republic of India as follows:-
PART I OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – PRELIMINARY
1. Short title.
This Act may be called the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019.
2. Definitions.
In this Act, unless the context otherwise requires,
(a) “appointed day” means the day* which the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, appoint;
* 31st October, 2019 —clause (a) of Section 2, vide notification No. S.O. 2889 (E), dated 09th August, 2016 see Gazette of India Extraordinary, Part II, s. 3 (ii)
(b) “article” means an article of the Constitution;
(c) “assembly constituency” and “parliamentary constituency” have the same meanings as in the Representation of the People Act, 1950 (43 of 1950);
(d) “Election Commission” means the Election Commission appointed by the President under article 324;
(e) “existing State of Jammu and Kashmir” means the State of Jammu and Kashmir as existing immediately before the appointed day, comprising the territory which immediately before the commencement of the Constitution of India in the Indian State of Jammu and Kashmir;
(f) “law” includes any enactment, ordinance, regulation, order, bye-law, rule, scheme, notification or other instrument having, immediately before the appointed day, the force of law in the whole or in any part of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir;
(g) “Legislative Assembly” means Legislative Assembly of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir;
(h) “Lieutenant Governor” means the Administrator of the Union territory appointed by the President under article 239;
(i) “notified order” means an order published in the Official Gazette;
(j) “population ratio”, in relation to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, and Union
territory of Ladakh means the ratio as per 2011 Census;
(k) “Scheduled Castes” in relation to the Union territory means such castes, races or tribes or parts of groups within such castes, races or tribes as are deemed under article 341 to be Scheduled Castes in relation to that Union territory;
(l) “Scheduled Tribes” in relation to the Union territory means such tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under article 342 to be Scheduled Tribes in relation to that Union territory;
(m) “sitting member”, in relation to either House of Parliament or of the Legislature of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir, means a person who immediately before the appointed day, is a member of that House;
(n) “Union territory”, in relation to the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir, means the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or Union territory of Ladakh, as the case may be;
(o) “transferred territory” means the territory which on the appointed day is transferred from the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir to Union territories formed under sections 3 and 4 of this Act; and
(p) any reference to a district, tehsil or other territorial division of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall be construed as a reference to the area comprised within that territorial division on the appointed day.
PART II OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – REORGANISATION OF THE STATE OF JAMMU AND KASHMIR
3. Formation of Union territory of Ladakh without Legislature.
On and from the appointed day, there shall be formed a new Union territory to be known as the Union territory of Ladakh comprising the following territories of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir, namely-
“Kargil and Leh districts”,
and thereupon the said territories shall cease to form part of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir.
4. Formation of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir with Legislature.
On and from the appointed day, there shall be formed a new Union territory to be known as the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir comprising the territories of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir other than those specified in section 3.
5. Governor of existing State of Jammu and Kashmir to be common Lieutenant Governor.
On and from the appointed day, the Governor of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall be the Lieutenant Governor for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, and Union territory of Ladakh for such period as may be determined by the President.
6. Amendment of First Schedule to the Constitution.
On and from the appointed day, in the First Schedule to the Constitution, under the heading—”I. THE STATES”,—
(a) entry 15 shall be deleted.
(b) entries from 16 to 29 shall be renumbered as 15 to 28.
(c) under the heading —”II. UNION TERRITORIES”,—
after entry 7, the following entries shall be inserted, namely:—
“8. Jammu and Kashmir: The territories specified in section 4 of the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019”.
“9. Ladakh: The territories specified in section 3 of the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019”.
7. Saving powers of the Government of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
Nothing in the foregoing provisions of this Part shall be deemed to affect the power of the Government of successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to alter, after the appointed day, the name, area or boundaries of any district or other territorial division in that Union territory.
PART III OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – REPRESENTATION IN THE LEGISLATURES
The Council of States
8. Amendment of Fourth Schedule to Constitution.
On and from the appointed day, in the Fourth Schedule to the Constitution, in the Table,-
(a) entry 21 shall be deleted;
(b) entries 22 to 31 shall be renumbered as entries 21 to 30, respectively;
(c) after entry 30, the following entry shall be inserted, namely:-
“31. Jammu and Kashmir …………………………………………..4”.
9. Allocation of sitting members.
(1) On and from the appointed day, four sitting members of the Council of States representing the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall be deemed to have been elected to fill the seats allotted to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, as specified in the First Schedule to this Act.
(2) The term of office of such sitting members shall remain unaltered.
The House of the People
10. Representation in House of the People.
On and from the appointed day, there shall be allocated five seats to the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and one seat to Union territory of Ladakh, in the House of the People, and the First Schedule to the Representation of the People Act, 1950 (43 of 1950) shall be deemed to be amended accordingly.
11. Delimitation of Parliamentary Constituencies order, 1976.
(1) On and from the appointed day, the Delimitation of Parliamentary Constituencies Order, 1976 shall stand amended as directed in the Second Schedule of this Act.
(2) The Election Commission may conduct the elections to the House of the People for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh as per the allocation of seats specified in the Delimitation of Parliamentary Constituencies Order, 1976 as amended by this Act.
12. Provision as to sitting members.
(1) Every sitting member of the House of the People representing a constituency which, on the appointed day by virtue of the provisions of section 10, stands allotted, with or without alteration of boundaries, to the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or Union territory of Ladakh, as the case may be, shall be deemed to have been elected to the House of the People by that constituency as so allotted.
(2) The term of office of such sitting members shall remain unaltered.
The Lieutenant Governor and The Legislative Assembly of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir
13. Applicability of article 239A of Constitution.
On and from the appointed day, the provisions contained in article 239A, which are applicable to “Union territory of Puducherry”, shall also apply to the “Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir”.
14. Legislative Assembly for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir and its composition.
(1) There shall be an Administrator appointed under article 239 of the Constitution of India for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and shall be designated as Lieutenant Governor of the said Union territory.
(2) There shall be a Legislative Assembly for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(3) The total number of seats in the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to be filled by persons chosen by direct election shall be 107.
(4) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (3), until the area of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir under the occupation of Pakistan ceases to be so occupied and the people residing in that area elect their representatives-
(a) twenty four seats in the Legislative Assembly of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall remain vacant and shall not be taken into account for reckoning the total membership of the Assembly; and
(b) the said area and seats shall be excluded in delimiting the territorial constituencies as provided under PART V of this Act.
(5) On and from the appointed day, the Delimitation of Assembly Constituencies Order, 1995, as applicable to Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, shall stand amended as directed in the Third Schedule of this Act.
(6) Seats shall be reserved for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(7) The number of seats reserved for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir under sub-section (6) shall bear, as nearly as may be, the same proportion to the total number of seats in the Assembly as the population of the Scheduled Castes in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or of the Scheduled Tribes in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, in respect of which seats are so reserved, bears to the total population of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
Explanation:
In this sub-section, the expression “population” means the population as ascertained at the last preceding census of which the relevant figures have been published:
Provided that the reference in this Explanation to the last preceding census of which the relevant figures have been published shall, until the relevant figures for the first census taken after the year 2026 have been published, be construed as a reference to the 2011 census.
(8) Notwithstanding anything in sub-section (6), the reservation of seats for the Scheduled Castes or Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall cease to have effect on the same date on which the reservation of seats for the Scheduled Castes or the Scheduled Tribes in the House of the People shall cease to have effect under article 334 of the Constitution of India.
(9) In the Second Schedule to the Representation of the People Act, 1950 (43 of 1950), under the heading :— “I. THE STATES:”
“(a) entry 10 shall be deleted”.
“(b) entries 11 to 29 shall be renumbered as 10 to 28”.
(10) In the Second Schedule to the Representation of the People Act, 1950 (43 of 1950), under the heading :—”II. UnionTerritories”
(a) after entry 2, the following entries shall be inserted, namely:-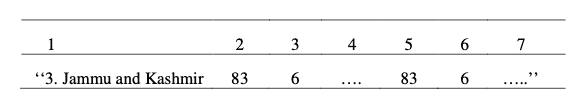
(11) The provisions of articles 324 to 327 and 329 of the Constitution of India, shall apply in relation to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, the Legislative Assembly and the members thereof as they apply, in relation to a State, the Legislative Assembly of a State and the members thereof respectively; and any reference in articles 326 and 329 to “appropriate Legislature” shall be deemed to be a reference to Parliament.
15. Representation of women.
Notwithstanding anything in sub-section (3) of section 14 the Lieutenant Governor of the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir may nominate two members to the Legislative Assembly to give representation to women, if in his opinion, women are not adequately represented in the Legislative Assembly.
16. Qualification for membership of Legislative Assembly.
A person shall not be qualified to be chosen to fill a seat in the Legislative Assembly unless he-
(a) is a citizen of India and makes and subscribes before some person authorised in that behalf by the Election Commission an oath or affirmation according to the form set out for the purpose in the Fourth Schedule of this Act;
(b) is not less than twenty-five years of age; and
(c) possesses such other qualifications as may be prescribed in that behalf by or under any
law made by the Parliament.
17. Duration of Legislative Assembly.
The Legislative Assembly, unless sooner dissolved, shall continue for five years from the date appointed for its first meeting and no longer, and the expiration of the said period of five years shall operate as a dissolution of the Legislative Assembly:
Provided that the said period may, while a Proclamation of Emergency issued under clause (1) of article 352 is in operation, be extended by the President by order for a period not exceeding one year at a time and not extending in any case beyond a period of six months after the Proclamation has ceased to operate.
18. Sessions of Legislative Assembly, prorogation and dissolution.
(1) The Lieutenant Governor shall, from time to time, summon the Legislative Assembly to meet at such time and place as he thinks fit, but six months shall not intervene between its last sitting in one session and the date appointed for its first sitting in the next session.
(2) The Lieutenant Governor may, from time to time,-
(a) prorogue the House;
(b) dissolve the Legislative Assembly.
19. Speaker and Deputy Speaker of Legislative Assembly.
(1) The Legislative Assembly shall, as soon as may be, choose two members of the Assembly to be respectively Speaker and Deputy Speaker thereof and, so often as the office of Speaker or Deputy Speaker becomes vacant, the Assembly shall choose another member to be Speaker or Deputy Speaker, as the case may be.
(2) A member holding office as Speaker or Deputy Speaker of the Assembly-
(a) shall vacate his office if he ceases to be a member of the Assembly;
(b) may at any time by writing under his hand addressed, if such member is the Speaker, to the Deputy Speaker, and if such member is the Deputy Speaker, to the Speaker, resign his office;
(c) may be removed from his office by a resolution of the Assembly passed by a majority of all the then members of the Assembly:
Provided that no resolution for the purpose of clause (c) shall be moved unless at least fourteen days’ notice has been given of the intention to move the resolution:
Provided further that, whenever the Assembly is dissolved, the Speaker shall not vacate his office until immediately before the first meeting of the Assembly after the dissolution.
(3) While the office of Speaker is vacant, the duties of the office shall be performed by the Deputy Speaker or, if the office of Deputy Speaker is also vacant, by such member of the Legislative Assembly as may be determined by the rules of procedure of the Assembly.
(4) During the absence of the Speaker from any sitting of the Legislative Assembly, the Deputy Speaker, or, if he is also absent, such person as may be determined by the rules of procedure of the Assembly, or, if no such person is present, such other person as may be determined by the Legislative Assembly, shall act as Speaker.
(5) There shall be paid to the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly, such salaries and allowances as may respectively be fixed by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir by law and, until provision in that behalf is so made, such salaries and allowances as the Lieutenant Governor may, by order determine.
20. Speaker or Deputy Speaker not to preside while a resolution for his removal from office is under consideration.
(1) At any sitting of the Legislative Assembly, while any resolution for the removal of the Speaker from his office is under consideration, the Speaker, or while any resolution for the removal of the Deputy Speaker, from his office is under consideration, the Deputy Speaker, shall not, though he is present, preside, and the provisions of sub-section (4) of section 19 shall apply in relation to every such sitting as they apply in relation to a sitting from which the Speaker or, as the case may be, the Deputy Speaker, is absent.
(2) The Speaker shall have the right to speak in, and otherwise to take part in the proceedings of, the Legislative Assembly while any resolution for his removal from office is under consideration in the Assembly and shall, notwithstanding anything in section 25, be entitled to vote only in the first instance on such resolution or on any other matter during such proceedings but not in the case of an equality of votes.
21. Special address by Lieutenant Governor to Legislative Assembly.
(1) At the commencement of the first session after each general election to the Legislative Assembly and at the commencement of the first session of each year, the Lieutenant Governor shall address the Legislative Assembly, and shall inform the Legislative Assembly of the causes of its summons.
(2) Provision shall be made by the rules regulating the procedure of the Legislative Assembly for the allotment of time for the discussion of matters referred to in such address.
22. Rights of Ministers and Advocate General as respects Legislative Assembly.
Every Minister and the Advocate-General for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall have the right to speak in, and otherwise to take part in the proceedings of, the Legislative Assembly, and to speak in, and otherwise to take part in the proceedings of, any committee of the Legislative Assembly of which he may be named a member, but shall not by virtue of this section be entitled to vote.
23. Rights of Lieutenant Governor to address and send messages to the Legislative Assembly.
(1) The Lieutenant Governor may address the Legislative Assembly and may for that purpose require the attendance of members.
(2) The Lieutenant Governor may also send messages to the Legislative Assembly whether with respect to a Bill then pending in the Legislative Assembly or otherwise, and when a message so sent, the Legislative Assembly shall with all convenient despatch consider any matter required by the message to be taken into consideration.
24. Oath or affirmation by members.
Every member of the Legislative Assembly shall, before taking his seat, make and subscribe before the Lieutenant Governor of the said Union territory, or some person appointed in that behalf by him, an oath or affirmation according to the form set out for the purpose in the Fourth Schedule of this Act.
25. Voting in Assembly, power of Assembly to act notwithstanding vacancies and quorum.
(1) Save as otherwise provided in this Act, all questions at any sitting of the Legislative Assembly shall be determined by a majority of votes of the members present and voting, other than the Speaker or person acting as such.
(2) The Speaker, or person acting as such, shall not vote in the first instance, but shall have and exercise a casting vote in the case of an equality of votes.
(3) The Legislative Assembly shall have power to act notwithstanding any vacancy in the membership thereof, and any proceedings in the Legislative Assembly shall be valid notwithstanding that it is discovered subsequently that some person who was not entitled so to do, sat or voted or otherwise took part in the proceedings.
(4) The quorum to constitute a meeting of the Legislative Assembly shall be ten members or one- tenth of the total number of members of the Legislative Assembly, which ever is greater.
(5) If at any time during a meeting of the Legislative Assembly there is no quorum, it shall be the duty of the Speaker, or person acting as such, either to adjourn the Legislative Assembly or to suspend the meeting until there is a quorum.
26. Vacation of seats.
(1) No person shall be a member both of Parliament and of the Legislative Assembly, and if a person is chosen a member both of Parliament and of such Assembly, then, at the expiration of such period as may be specified in the rules made by the President, that person’s seat in Parliament shall become vacant, unless he has previously resigned his seat in the Legislative Assembly of the said Union territory.
(2) If a member of the Legislative Assembly-
(a) becomes subject to any of disqualification mentioned in section 27 or section 28 for
membership of the Legislative Assembly; or
(b) resigns his seat by writing under his hand addressed to the Speaker, and his resignation is accepted by the Speaker, his seat shall thereupon become vacant.
(3) If for a period of sixty days a member of the Legislative Assembly is without permission of the Assembly absent from all meetings thereof, the Assembly may declare his seat vacant:
Provided that in computing the said period of sixty days, no account shall be taken of any period during which the Assembly is prorogued or is adjourned for more than four consecutive days.
27. Disqualifications for membership.
(1) A person shall be disqualified for being chosen as, and for being, a member of the Legislative Assembly-
(a) if he holds any office of profit under the Government of India or the Government of any State or the Government of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or the Government or administration of any other Union territory or other than an office declared by law made by Parliament or by the Legislative Assembly not to disqualify its holder; or
(b) if he is for the time being disqualified for being chosen as, and for being, a member of either House of Parliament under the provisions of sub-clause (b), sub-clause (c) or sub-clause (d) of clause (1) of article 102 or of any law made in pursuance of that article.
(2) For the purposes of this section, a person shall not be deemed to hold an office of profit under the Government of India or the Government of any State or the Government of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or the Government of any other Union territory by reason only that he is a Minister either for the Union or for such State or Union territory.
(3) If any question arises as to whether a member of the Legislative Assembly becomes subject to any of disqualification under the provisions of sub-sections (1) and (2), the question shall be referred for the decision of the Lieutenant Governor and his decision shall be final.
(4) Before giving any decision on any such question, the Lieutenant Governor shall obtain the opinion of the Election Commission and shall act according to such opinion.
28. Disqualification on ground of defection for being a member.
The provisions of the Tenth Schedule to the Constitution shall, subject to the necessary modifications (including modifications for construing references therein to the Legislative Assembly of a State, article 188, article 194 and article 212 as references, respectively, to the Legislative Assembly of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, as the case may be, section 24, section 30 and section 50 of this Act), apply to and in relation to the members of the Legislative Assembly of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir as they apply to and in relation to the members of the Legislative Assembly of a State, and accordingly,-
(a) the said Tenth Schedule as so modified shall be deemed to form part of this Act; and
(b) a person shall be disqualified for being a member of the Legislative Assembly if he is so
disqualified under the said Tenth Schedule as so modified.
29. Penalty for sitting and voting before making oath or affirmation or when not qualified or when disqualified.
If a person sits or votes as a member of the Legislative Assembly before he has complied with the requirements of section 24 or when he knows that he is not qualified or that he is disqualified for membership thereof, or that he is prohibited from doing so by the provisions of any law made by Parliament or the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, he shall be liable in respect of each day on which he so sits or votes to a penalty of five hundred rupees to be recovered as a debt due to the said Union territory.
30. Powers, privileges, etc., of members.
(1) Subject to the provisions of this Act and to the rules and standing orders regulating the procedure of the Legislative Assembly, there shall be freedom of speech in the Legislative Assembly.
(2) No member of the Legislative Assembly shall be liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said or any vote given by him in the Assembly or any committee thereof, and no person shall be so liable in respect of the publication by or under the authority of such Assembly of any report, paper, votes or proceedings.
(3) In other respects, the powers, privileges and immunities of the Legislative Assembly and of the members and the committees thereof shall be such as are for the time being enjoyed by the House of the People and its members and committees.
(4) The provisions of sub-sections (1), (2) and (3) shall apply in relation to persons who by virtue of this Act have the right to speak in, and otherwise to take part in the proceedings of, the Legislative Assembly or any committee thereof as they apply in relation to members of the Legislative Assembly.
31. Salaries and allowances of members.
Members of the Legislative Assembly shall be entitled to receive such salaries and allowances as may from time to time be determined by the Legislative Assembly by law and, until provision in that behalf is so made, such salaries and allowances as the Lieutenant Governor may, by order determine.
32. Extent of legislative power.
(1) Subject to the provisions of this Act, the Legislative Assembly may make laws for the whole or any part of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir with respect to any of the matters enumerated in the State List except the subjects mentioned at entries 1 and 2, namely “Public Order” and “Police” respectively or the Concurrent List in the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India in so far as any such matter is applicable in relation to the Union territories.
(2) Nothing in sub-section (1) shall derogate from the powers conferred on Parliament by the Constitution to make laws with respect to any matter for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or any part thereof.
33. Exemption of property of the Union from taxation.
The property of the Union shall, save in so far as Parliament may by law otherwise provide, be exempted from all taxes imposed by or under any law made by the Legislative Assembly or by or under any other law in force in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir:
Provided that nothing in this section shall, until Parliament by law otherwise provides, prevent any authority within the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir from levying any tax on any property of the Union to which such property was immediately before the commencement of the Constitution liable or treated as liable, so long as that tax continues to be levied in that Union territory.
34. Restrictions on laws passed by Legislative Assembly with respect to certain matters.
(1) The provisions of article 286, article 287 and article 288 shall apply in relation to any law passed by the Legislative Assembly with respect to any of the matters referred to in those articles as they apply in relation to any law passed by the Legislature of a State with respect to those matters.
(2) The provisions of article 304 shall, with the necessary modifications, apply in relation to any law passed by the Legislative Assembly with respect to any of the matters referred to in that article as they apply in relation to any law passed by the Legislature of a State with respect to those matters.
35. Inconsistency between laws made by Parliament and laws made by Legislative Assembly.
If any provision of a law made by the Legislative Assembly with respect to matters enumerated in the State List, in the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution is repugnant to any provision of a law made by Parliament with respect to that matter, whether passed before or after the law made by the Legislative Assembly, or, if any provision of a law made by the Legislative Assembly with respect to any matter enumerated in the Concurrent List in the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution is repugnant to any provision of any earlier law, other than a law made by the Legislative Assembly, with respect to that matter, then, in either case, the law made by Parliament, or, as the case may be, such earlier law shall prevail and the law made by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory shall, to the extent of the repugnancy, be void:
Provided that if such law made by the Legislative Assembly has been reserved for the consideration of the President and has received his assent, such law shall prevail in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir:
Provided further that nothing in this section shall prevent Parliament from enacting at any time any law with respect to the same matter including a law adding to, amending, varying or repealing the law so made by the Legislative Assembly.
36. Special provisions as to financial Bills.
(1) A Bill or amendment shall not be introduced into, or moved in, the Legislative Assembly except on the recommendation of the Lieutenant Governor, if such Bill or Amendment makes provision for any of the following matters, namely:-
(a) the imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of any tax;
(b) the amendment of the law with respect to any financial obligations undertaken or to be
undertaken by the Government of the Union territory;
(c) the appropriation of moneys out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory;
(d) the declaring of any expenditure to be expenditure charged on the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory or the increasing of the amount of any such expenditure;
(e) the receipt of money on account of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory or the public account of the Union territory or the custody or issue of such money or the audit of the account of the Union territory:
Provided that no recommendation shall be required under this sub-section for the moving of an amendment making provision for the reduction or abolition of any tax.
(2) A Bill or Amendment shall not be deemed to make provision for any of the matters aforesaid by reason only that it provides for the imposition of fines or other pecuniary penalties, or for the demand or payment of fees for licences or fees for services rendered, or by reason that it provides for the imposition, abolition, remission, alteration or regulation of any tax by any local authority or body for local purposes.
(3) A Bill which, if enacted and brought into operation, would involve expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of Union territory shall not be passed by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory unless the Lieutenant Governor has recommended to the Assembly, the consideration of the Bill.
37. Procedure as to lapsing of Bills.
(1) A Bill pending in the Legislative Assembly shall not lapse by reason of the prorogation of the Legislative Assembly.
(2) A Bill which is pending in the Legislative Assembly shall lapse on dissolution of the Legislative Assembly.
38. Assent to Bills.
When a Bill has been passed by the Legislative Assembly, it shall be presented to the Lieutenant Governor and the Lieutenant Governor shall declare either that he assents to the Bill or that he withholds assent therefrom or that he reserves the Bill for the consideration of the President:
Provided that the Lieutenant Governor may, as soon as possible after the presentation of the Bill to him for assent, return the Bill if it is not a Money Bill together with a message requesting that the Assembly will reconsider the Bill or any specified provisions thereof, and, in particular, will consider the desirability of introducing any such amendments as he may recommend in his message and, when a Bill is so returned, the Assembly will reconsider the Bill accordingly, and if the Bill is passed again with or without amendment and presented to the Lieutenant Governor for assent, the Lieutenant Governor shall declare either that he assents to the Bill or that he reserves the Bill for the consideration of the President:
Provided further that the Lieutenant Governor shall not assent to, but shall reserve for the consideration of the President, any Bill which,-
(a) in the opinion of the Lieutenant Governor would, if it became law, so derogate from the powers of the High Court as to endanger the position which that Court is, by the Constitution, designed to fill; or
(b) relates to any of the matters specified in clause (1) of article 31A; or
(c) the President may, by order, direct to be reserved for his consideration.
Explanation:
For the purposes of this section and section 39, a Bill shall be deemed to be a Money Bill if it contains only provisions dealing with all or any of the matters specified in sub-section (1) of section 36 or any matter incidental to any of those matters and, in either case, there is endorsed thereon the certificate of the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly signed by him that it is a Money Bill.
39. Bills reserved for consideration.
When a Bill is reserved by Lieutenant Governor for the consideration of the President, the President shall declare either that he assents to the Bill or that he withholds assent therefrom:
Provided that where the Bill is not a Money Bill, the President may direct the Lieutenant Governor to return the Bill to the Legislative Assembly together with such a message as is mentioned in the first proviso to section 38 and, when a Bill is so returned, the Assembly shall reconsider it accordingly within a period of six months from the date of receipt of such message and, if it is again passed by the Assembly with or without amendment, it shall be presented again to the President for his consideration.
40. Requirements as to sanction and recommendations to be regarded as matters of procedure only.
No Act of the Legislative Assembly and no provision in any such Act, shall be invalid by reason only that some previous sanction or recommendation required by this Act was not given, if assent to that Act was given by the Lieutenant Governor, or, on being reserved by the Lieutenant Governor for the consideration of the President, by the President.
41. Annual financial statement.
(1) The Lieutenant Governor shall in respect of every financial year cause to be laid before the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, a statement of the estimated receipts and expenditure of the Union territory for that year, in this Part referred to as the “annual financial statement”.
(2) The estimates of expenditure embodied in the annual financial statement shall show separately-
(a) the sums required to meet expenditure described by this Act as expenditure charged upon the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, and
(b) the sums required to meet other expenditure proposed to be made from the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir; and shall distinguish expenditure on revenue account from other expenditure.
(3) The following expenditure shall be expenditure charged on the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir:-
(a) the emoluments and allowances of the Lieutenant Governor and other expenditure relating to his office;
(b) the charges payable in respect of loans advanced to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir from the Consolidated Fund of India including interest, sinking fund charges and redemption charges, and other expenditure connected therewith;
(c) the salaries and allowances of the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly;
(d) expenditure in respect of the salaries and allowances of Judges of High Court of Jammu and Kashmir;
(e) any sums required to satisfy any judgment, decree or award of any court or arbitral tribunal;
(f) expenditure incurred by the Lieutenant Governor in the discharge of his special
responsibility;
(g) any other expenditure declared by the Constitution or by law made by Parliament or by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to be so charged.
42. Procedure in Legislative Assembly with respect to estimates.
(1) So much of the estimates as relates to expenditure charged upon the Consolidated Fund of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall not be submitted to the vote of the Legislative Assembly, but nothing in this sub-section shall be construed as preventing the discussion in the Legislative Assembly of any of those estimates.
(2) So much of the said estimates as relates to other expenditure shall be submitted in the form of demands for grants to the Legislative Assembly, and the Legislative Assembly shall have power to assent, or to refuse to assent, to any demand, or to assent to any demand subject to a reduction of the amount specified therein.
(3) No demand for a grant shall be made except on the recommendation of the Lieutenant Governor.
43. Appropriation Bills.
(1) As soon as may be after the grants under section 42 have been made by the Legislative Assembly, there shall be introduced a Bill to provide for the appropriation out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of all moneys required to meet-
(a) the grants so made by the Legislative Assembly, and
(b) the expenditure charged on the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir but not exceeding in any case the amount shown in the statement previously laid before the Assembly.
(2) No amendment shall be proposed to any such Bill in the Legislative Assembly which will have the effect of varying the amount or altering the destination of any grant so made or of varying the amount of any expenditure charged on the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and the decision of the person presiding as to whether an amendment is inadmissible under this sub-section shall be final.
(3) Subject to the other provisions of this Act, no money shall be withdrawn from the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory except under appropriation made by law passed in accordance with the provisions of this section.
44. Supplementary, additional or excess grants.
(1) The Lieutenant Governor shall-
(a) if the amount authorised by any law made in accordance with the provisions of section 43 to be expended for a particular service for the current financial year is found to be insufficient for the purposes of that year or when a need has arisen during the current financial year for supplementary or additional expenditure upon some new service not contemplated in the annual financial statement for that year, or
(b) if any money has been spent on any service during a financial year in excess of the amount granted for that service and for that year,
cause to be laid before the Legislative Assembly, another statement showing the estimated amount of that expenditure or cause to be presented to the Legislative Assembly with such previous approval a demand for such excess, as the case may be.
(2) The provisions of sections 41, 42 and 43 shall have effect in relation to any such statement and expenditure or demand and also to any law to be made authorising the appropriation of moneys out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to meet such expenditure or the grant in respect of such demand as they have effect in relation to the annual financial statement and the expenditure mentioned therein or to a demand for a grant and the law to be made for the authorisation of appropriation of moneys out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to meet such expenditure or grant.
45. Votes on account.
(1) Notwithstanding anything in the foregoing provisions of this Part, the Legislative Assembly shall have power to make any grant in advance in respect of the estimated expenditure for a part of any financial year pending the completion of the procedure prescribed in section 42 for the voting of such grant and the passing of the law in accordance with the provisions of section 43 in relation to that expenditure and the Legislative Assembly shall have power to authorise by law the withdrawal of moneys from the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir for the purposes for which the said grant is made.
(2) The provisions of sections 42 and 43 shall have effect in relation to the making of any grant under sub-section (1) or to any law to be made under that sub-section as they have effect in relation to the making of a grant with regard to any expenditure mentioned in the annual financial statement and the law to be made for the authorisation of appropriation of moneys out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to meet such expenditure.
46. Rules of procedure.
(1) The Legislative Assembly may make rules for regulating, subject to the provisions of this Act, its procedure and the conduct of its business:
Provided that the Lieutenant Governor shall, after consultation with the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly, make rules-
(a) for securing the timely completion of financial business;
(b) for regulating the procedure of, and the conduct of business in, the Legislative Assembly in relation to any financial matter or to any Bill for the appropriation of moneys out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir;
(c) for prohibiting the discussion of, or the asking of questions on, any matter which affects the discharge of the functions of the Lieutenant Governor in so far as he is required by this Act to act in his discretion.
(2) Until rules are made under sub-section (1), the rules of procedure and standing orders in force immediately before the commencement of this Act, with respect to the Legislative Assembly of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall have effect in relation to the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir subject to such modifications and adaptations as may be made therein by the Speaker of Legislative Assembly.
47. Official language or languages of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and language or languages to be used in Legislative Assembly thereof.
(1) The Legislative Assembly may by law adopt any one or more of the languages in use in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or Hindi as the official language or languages to be used for all or any of the official purposes of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(2) The business in the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall be transacted in the official language or languages of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or in Hindi or in English:
Provided that the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly or person acting as such, as the case may be, may permit any member who cannot adequately express himself in any of the languages aforesaid to address the Legislative Assembly in his mother tongue.
48. Language to be used for Acts, Bills, etc.
Notwithstanding anything contained in section 47, until Parliament by law otherwise provides, the authoritative texts-
(a) of all Bills to be introduced or amendments thereto to be moved in the Legislative Assembly,
(b) of all Acts passed by the Legislative Assembly, and
(c) of all orders, rules, regulations and bye-laws issued under any law made by the Legislative
Assembly,
shall be in the English language:
Provided that where the Legislative Assembly has prescribed any language other than the English language for use in Bills introduced in, or Acts passed by, the Legislative Assembly or in any order, rule, regulation or bye-law issued under any law made by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, a translation of the same in the English language published under the authority of the Lieutenant Governor in the Official Gazette shall be deemed to be the authoritative text thereof in the English language.
49. Restriction on discussion in the Legislative Assembly.
No discussion shall take place in the Legislative Assembly with respect to the conduct of any judge of the Supreme Court or of a High Court in the discharge of his duties.
50. Courts not to inquire into proceedings of Legislative Assembly.
(1) The validity of any proceedings in the Legislative Assembly shall not be called in question on the ground of any alleged irregularity of procedure.
(2) No officer or member of the Legislative Assembly in whom powers are vested by or under this Act for regulating procedure or the conduct of business, or for maintaining order in the Legislative Assembly shall be subject to the jurisdiction of any court in respect of the exercise by him of those powers.
51. Secretariat of the Legislative Assembly.
(1) The Legislative Assembly shall have a separate secretariat staff.
(2) The Legislative Assembly may by law regulate the recruitment, and the conditions of service of persons appointed, to the secretarial staff of the Legislative Assembly.
(3) Until provision is made by the Legislative Assembly under sub-section (2), the Lieutenant Governor may, after consultation with the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly make rules regulating the recruitment, and the conditions of service of persons appointed, to the secretarial staff of the Assembly and any rules so made shall have effect subject to the provisions of any law made under the said sub-section.
52. Power of Lieutenant Governor to promulgate Ordinances during recess of Legislative Assembly.
(1) If at any time, except when the Legislative Assembly is in session, the Lieutenant Governor thereof is satisfied that circumstances exist which render it necessary for him to take immediate action, he may promulgate such Ordinances as the circumstances appear to him to require:
Provided that the power of making an Ordinance under this section shall extend only to those matters with respect to which the Legislative Assembly has power to make laws.
(2) An Ordinance promulgated under this section shall have the same force and effect as an Act of the Legislative Assembly assented by the Lieutenant Governor but every such Ordinance-
(a) Shall be laid before the Legislative Assembly and shall cease to operate at the expiration of six weeks from the re-assembly of the Legislative Assembly, or if before the expiration of that period a resolution disapproving it is passed by the Legislative Assembly; and
(b) May be withdrawn at any time by the Lieutenant Governor.
Council of Ministers for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir
53. Council of Ministers.
(1) There shall be a Council of Ministers consisting of not more than ten per cent. of the total number of members in the Legislative Assembly, with the Chief Minister at the head to aid and advise the Lieutenant Governor in the exercise of his functions in relation to matters with respect to which the Legislative Assembly has power to make laws except in so far as he is required by or under this Act to act in his discretion or by or under any law to exercise any judicial or quasi-judicial functions.
(2) The Lieutenant Governor shall, in the exercise of his functions, act in his discretion in a matter:
(i) which falls outside the purview of the powers conferred on the Legislative Assembly; or
(ii) in which he is required by or under any law to act in his discretion or to exercise any judicial functions; or
(iii) related to All India Services and Anti Corruption Bureau:
Provided that if any question arises whether any matter is or is not a matter as respects which the Lieutenant Governor is by or under this Act required to act in his discretion, the decision of the Lieutenant Governor in his discretion shall be final, and the validity of anything done by the Lieutenant Governor shall not be called in question on the ground that he ought or ought not to have acted in his discretion.
(3) The question whether any, and if so what, advice was tendered by Ministers to the Lieutenant Governor shall not be inquired into in any court.
54. Other provisions as to Ministers.
(1) The Chief Minister shall be appointed by the Lieutenant Governor and the other Ministers shall be appointed by the Lieutenant Governor on the advice of the Chief Minister.
(2) The Ministers shall hold office during the pleasure of the Lieutenant Governor.
(3) The Council of Ministers shall be collectively responsible to the Legislative Assembly.
(4) Before a Minister enters upon his office, the Lieutenant Governor shall administer to him the oaths of office and of secrecy according to the forms set out for the purpose in the Fourth Schedule to this Act.
(5) A Minister who for any period of six consecutive months is not a member of the Legislative Assembly shall at the expiration of that period cease to be a Minister.
(6) The salaries and allowances of Ministers shall be such as the Legislative Assembly may from time to time by law determine, and until the Legislative Assembly so determines, shall be determined by the Lieutenant Governor.
55. Conduct of business.
(1) The Lieutenant Governor shall make rules on the advice of the Council of Ministers-
(a) for the allocation of business to the Ministers; and
(b) for the more convenient transaction of business with the Ministers including the procedure to be adopted in case of a difference of opinion between the Lieutenant Governor and the Council of Ministers or a Minister.
(2) Save as otherwise provided in this Act, all executive action of the Lieutenant Governor, whether taken on the advice of his Ministers or otherwise, shall be expressed to be taken in the name of the Lieutenant Governor.
(3) Orders and other instruments made and executed in the name of the Lieutenant Governor, shall be authenticated in such manner as may be specified in rules to be made by the Lieutenant Governor on the advice of Council of Ministers, and the validity of an order or instrument which is so authenticated shall not be called in question on the ground that it is not an order or instrument made or executed by the Lieutenant Governor.
56. Duties of Chief Minister as respects the furnishing of information to the Lieutenant Governor, etc.
It shall be the duty of the Chief Minister-
(a) to communicate to the Lieutenant Governor all decisions of the Council of Ministers relating to the administration of the affairs of the Union territory and proposals for legislation;
(b) to furnish such information relating to the administration of the affairs of the Union territory and proposals for legislation as Lieutenant Governor may call for.
Legislative Council
57. Abolition of Legislative Council of the State of Jammu and Kashmir.
(1) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained in any law, document, judgment, ordinance, rule, regulation or notification, on and from the appointed day, the Legislative Council of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall stand abolished.
(2) On the abolition of the Legislative Council, every member thereof shall cease to be such member.
(3) All Bills pending in the Legislative Council immediately before the appointed day shall lapse on the abolition of the Council.
PART IV OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – ADMINISTRATION OF UNION TERRITORY OF LADAKH
58. Appointment of Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Ladakh.
(1) The Union territory of Ladakh will be administered by the President acting, to such extent as he thinks fit, through a Lieutenant Governor to be appointed by him under article 239.
(2) The President may make regulations for the peace, progress and good government of the Union territory of Ladakh under article 240 of the Constitution of India.
(3) Any regulation so made may repeal or amend any Act made by Parliament or any other law which is for the time being applicable to the Union territory of Ladakh and, when promulgated by the President, shall have the same force and effect as an Act of Parliament which applies to the Union territory of Ladakh.
(4) The Lieutenant Governor shall be assisted by advisor(s) to be appointed by the Central Government.
PART V OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – DELIMITATION OF CONSTITUENCIES
59. Definitions.
In this Part, unless the context otherwise requires,-
(a) “associate member” means a member associated with the Delimitation Commission under section 60;
(b) “Delimitation Commission” means the Delimitation Commission to be constituted under section 3 of the Delimitation Act, 2002 (33 of 2002); and thereafter by any law made by the Parliament.
(c) “Election Commission” means the Election Commission appointed by the President under article 324 of the Constitution of India;
(d) “latest census figures” mean the census figures ascertained at the latest census of which the finally published figures are available;
(e) “Parliamentary Constituency” means a constituency provided by law for the purpose of elections to the House of the People from Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh.
(f) “Assembly Constituency” means a constituency provided by law for the purpose of elections to the Legislative Assembly.
60. Delimitation of constituencies.
(1) Without prejudice to sub-sections (3) of section 14 of this Act, the number of seats in the Legislative Assembly of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall be increased from 107 to 114, and delimitation of the constituencies may be determined by the Election Commission in the manner hereinafter provided-
(a) the number of seats to be reserved for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative Assembly, having regard to the relevant provisions of the Constitution;
(b) the assembly constituencies into which the Union territory shall be divided, the extent of each of such constituencies and in which of them seats shall be reserved for the Scheduled Castes or for the Scheduled Tribes; and
(c) the adjustments in the boundaries and description of the extent of the parliamentary constituencies in each Union territory that may be necessary or expedient.
(2) In determining the matters referred to in clauses (b) and (c) of sub-section (1), the Election Commission shall have regard to the following provisions, namely:-
(a) all the constituencies shall be single-member constituencies;
(b) all constituencies shall, as far as practicable, be geographically compact areas, and in delimiting them, regard shall be had to physical features, existing boundaries of administrative units, facilities of communication and conveniences to the public; and
(c) constituencies in which seats are reserved for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes shall, as far as practicable, be located in areas where the proportion of their population to the total population is the largest.
(3) The Election Commission shall, for the purpose of assisting it in the performance of its functions under sub-section (1), associate with itself as associate members, four persons as the Central Government may by order specify, being persons who are the members of the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or four members of the House of the People representing the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir:
Provided that none of the associate members shall have a right to vote or to sign any decision of the Election Commission.
(4) If, owing to death or resignation, the office of an associate member falls vacant, it shall be filled as far as practicable, in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (3).
(5) The Election Commission shall-
(a) publish its proposals for the delimitation of constituencies together with the dissenting proposals, if any, of any associate member who desires publication thereof in the Official Gazette and in such other manner as the Commission may consider fit, together with a notice inviting objections and suggestions in relation to the proposals and specifying a date on or after which the proposals will be further considered by it;
(b) consider all objections and suggestions which may have been received by it before the date so specified; and
(c) after considering all objections and suggestions which may have been received by it before the date so specified, determine by one or more orders the delimitation of constituencies and cause such order or orders to be published in the Official Gazette, and there upon such publication, the order or orders shall have the full force of law and shall not be called in question in any court.
(6) As soon as may be after such publication, every such order relating to assembly constituencies shall be laid before the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
61. Power of Election Commission to maintain Delimitation Orders up-to-date.
(1) The Election Commission may by notification in the Official Gazette,-
(a) correct any printing mistakes in any order made under section 60 or any error arising therein from inadvertent slip or omission; and
(b) where the boundaries or name of any territorial division mentioned in any such order or orders is or are altered, make such amendments as appear to it to be necessary or expedient for bringing such order up-to-date.
(2) Every notification under this section relating to an assembly constituency shall be laid, as soon as may be after it is issued, before the Legislative Assembly.
62. Special provision as to readjustment of Parliamentary and Assembly Constituencies on the basis of 2011 census.
(1) On and from the appointed day, notwithstanding the publication of orders under sub-section (1) of section 10 of the Delimitation Act, 2002 (33 of 2002) or anything contained in sub-section (2) or sub-section (4) of the said section, the Delimitation Act, 2002 shall be deemed to have been amended as provided below:
(a) in section 2, in clause (f), the words “but does not include the State of Jammu and Kashmir” shall be omitted; and
(b) for the purpose of delimitation of Assembly and Parliamentary Constituencies, the words and figures “census held in the year 2001”, wherever occurring, shall be construed as words and figures “census held in the year 2011”.
(2) Readjustment of the constituencies as provided under section 60 in the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir into Assembly Constituencies, shall be carried by the Delimitation Commission, to be constituted under the Delimitation Act, 2002 (33 of 2002) as amended by this Act, and shall take effect from such date as the Central Government may, by order, publish in the Official Gazette, specify.
(3) Readjustment of the constituencies as provided under section 11 in the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir into Parliamentary Constituencies, shall be carried by the Delimitation Commission, to be constituted under the Delimitation Act, 2002 (33 of 2002) as amended by this Act, and shall take effect from such date as the Central Government may, by order, publish in the Official Gazette, specify.
63. Special provisions as to readjustment of Assembly and Parliamentary Constituencies.
Notwithstanding anything contained in sections 59 to 61, until the relevant figures for the first census taken after the year 2026 have been published, it shall not be necessary to readjust the division of successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir into Assembly and Parliamentary Constituencies and any reference to the “latest census figures” in this Part shall be construed as a reference to the 2011 census figures.
64. Procedure as to delimitation.
The procedure as provided in the law made by Parliament, shall apply, in relation to the delimitation of Parliamentary and Assembly constituencies under this Part as they apply in relation to the delimitation of Parliamentary and Assembly constituencies under that law.
PART VI OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – SCHEDULED CASTES AND SCHEDULED TRIBES
65. Applicability of Scheduled Castes Order.
On and from the appointed day, the Constitution Jammu and Kashmir (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1956 [Jammu and Kashmir (Schedule Castes Order, 1956)], shall stand applied to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh.
66. Applicability of Scheduled Tribes Order.
On and from the appointed day, the Constitution Jammu and Kashmir (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1989, [Jammu and Kashmir (Scheduled Tribes Order, 1989)] shall stand applied to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh.
PART VII OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – MISCELLANEOUS AND TRANSITIONAL PROVISIONS
67. Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(1) On and from the appointed day, all revenues received in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir by the Government of India or the Lieutenant Governor of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir in relation to any matter with respect to which the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir has power to make laws, and all grants made and all loans advanced to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir from the Consolidated Fund of India and all loans raised by the Government of India or the Lieutenant Governor of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir upon the security of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and all moneys received by the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir in repayment of loans shall form one Consolidated Fund to be entitled “the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir”.
(2) No moneys out of such Consolidated Fund shall be appropriated except in accordance with, and for the purposes and in the manner provided in, this Act.
(3) The custody of such Consolidated Fund, the payment of moneys into such Funds, the withdrawal of moneys therefrom and all other matters connected with or ancillary to those matters shall be regulated by rules made by the Lieutenant Governor.
68. Public Account of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and moneys credited to it.
(1) On and from the appointed day, all other public moneys received by or on behalf of the Lieutenant Governor shall be credited to a Public Account entitled “the Public Account of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir”.
(2) The custody of public moneys, other than those credited to the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory or the Contingency Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, received by or on behalf of the Lieutenant Governor, their payment into the Public Accounts of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and the withdrawal of moneys from such account and all other matters connected with or ancillary to the aforesaid matters shall be regulated by rules made by the Lieutenant Governor on the advice of Council of Ministers.
69. Contingency Fund of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(1) There shall be established a Contingency Fund in the nature of an imprest to be entitled “the Contingency Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir”, into which shall be paid from and out of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir such sums as may, from time to time, be determined by law made by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir; and the said Fund shall be held by the Lieutenant Governor to enable advances to be made by him out of such Fund.
(2) No advances shall be made out of the Contingency Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir except for the purposes of meeting unforeseen expenditure pending authorisation of such expenditure by the Legislative Assembly under appropriations made by law.
(3) The Lieutenant Governor on the advice of the Council of Ministers may make rules regulating all matters connected with or ancillary to the custody of, the payment of moneys into, and the withdrawal of moneys from, the Contingency Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
70. Borrowing upon the security of Consolidated Fund of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(1) The executive power of the Union territory extends to borrowing upon the security of the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir within such limits, if any, as may, from time to time, be fixed by Legislative Assembly by law and to the giving of guarantees within such limits, if any, as may be so fixed.
(2) Any sums required for the purpose of invoking a guarantee shall be charged on the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
71. Form of accounts of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
The accounts of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall be kept in such form as the Lieutenant Governor may, after obtaining advice of the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India, prescribe by rules.
72. Audit reports.
The reports of the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India relating to the accounts of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir for any period subsequent to the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 67 shall be submitted to the Lieutenant Governor who shall cause them to be laid before the Legislative Assembly.
73. Provision in case of failure of constitutional machinery.
If the President, on receipt of a report from the Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, or otherwise, is satisfied,-
(a) that a situation has arisen in which the administration of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Act, or
(b) that for the proper administration of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir it is necessary or expedient so to do,
the President may, by order, suspend the operation of all or any of the provisions of this Act for such period as he thinks fit and make such incidental and consequential provisions as may appear to him to be necessary or expedient for administering the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir in accordance with the provisions of this Act.
74. Authorisation of expenditure by President.
Where the Legislative Assembly is dissolved, or its functioning as such Assembly remains suspended, on account of an order under section 73, it shall be competent for the President to authorise, when the House of the People is not in Session, expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir pending the sanction of such expenditure by Parliament.
PART VIII OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – HIGH COURT
75. High Court of Jammu and Kashmir to be common High Court.
(1) On and from the appointed day,-
(a) the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir shall be the common High Court for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh;
(b) the Judges of the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir for the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir holding office immediately before the appointed day shall become on that day the Judges of the common High Court.
(2) The expenditure in respect of salaries and allowances of the Judges of the common High Court shall be allocated amongst the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh on the basis of population ratio.
76. Special provision relating to Bar Council and advocates.
(1) On and from the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75, in the Advocates Act, 1961 (25 of 1961), in section 3, in sub-section (1),-
(a) in clause (a), the words “Jammu and Kashmir” shall be deleted.
(b) after clause (f), the following clause shall be inserted, namely-
-(g)- for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh, to be known as the Bar Council of Jammu and Kashmir; and Ladakh.
(2) Any person who immediately before the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75 is an advocate on the roll of the Bar Council of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir and practising as an advocate in the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir, may continue to be members of the “Bar council of Jammu and Kashmir; and Ladakh’’, notwithstanding anything contained in the Advocates Act, 1961 and the rules made thereunder.
(3) The persons other than the advocates who are entitled immediately before the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75, on and after that date, be recognised as such persons entitled also to practise in the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir or any subordinate court thereof, as the case may be.
(4) The right of audience in the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir shall be regulated in accordance with the like principles as immediately before the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75, are in force with respect to the right of audience in the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir.
77. Practice and procedure in common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir.
Subject to the provisions of this Part, the law in force immediately before the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75 with respect to practice and procedure in the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir shall, with the necessary modifications, apply in relation to the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir and accordingly, the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir shall have all such powers to make rules and orders with respect to practice and procedure as are immediately before that date exercisable by the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir:
Provided that any rules or orders which are in force immediately before the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75 with respect to practice and procedure in the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir shall, until varied or revoked by rules or orders made by the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir, apply with the necessary modifications in relation to practice and procedure in the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir as if made by that Court.
78. Savings.
Nothing in this Part shall affect the application to the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir of any provisions of the Constitution, and this Part shall have effect subject to any provision that may be made on or after the date referred to in sub-section (1) of section 75 with respect to the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir by any Legislature or other authority having power to make such provision.
PART IX OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – ADVOCATE-GENERAL OF UNION TERRITORY OF JAMMU AND KASHMIR
79. Advocate General for Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(1) The Lieutenant Governor shall appoint a person who is qualified to be appointed a Judge of the High Court, to be Advocate-General for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(2) It shall be the duty of such Advocate-General to give advice to the Government of such Union territory upon such legal matters and to perform such other duties of a legal character, as may from time to time be referred or assigned to him by the said Government, and to discharge the functions conferred on him by or under the Constitution or any other law for the time being in force.
(3) In the performance of his duties, the Advocate-General shall have the right of audience in all courts in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(4) The Advocate-General shall hold office during the pleasure of the Lieutenant Governor and receive such remuneration as the Lieutenant Governor may determine.
PART X OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – AUTHORISATION OF EXPENDITURE AND DISTRIBUTION OF REVENUES
80. Authorisation of expenditure of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
The Governor of existing State of Jammu and Kashmir may, at any time before the appointed day, authorise such expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir as he deems necessary for any period not more than six months beginning with the appointed day pending the sanction of such expenditure by the Legislative Assembly of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir:
Provided that the Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir may, after the appointed day, authorise such further expenditure as he deems necessary from the Consolidated Fund of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir for any period not extending beyond the said period of six months.
81. Authorisation of expenditure of Union territory of Ladakh.
The Governor of existing State of Jammu and Kashmir may, at any time before the appointed day, authorise such expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir as he deems necessary for any period not more than six months beginning with the appointed day pending the sanction of such expenditure by the Parliament:
Provided that the President may, after the appointed day, authorise such further expenditure as he deems necessary from the Consolidated Fund of India for any period not extending beyond the said period of six months.
82. Reports relating to accounts of Jammu and Kashmir State.
(1) The reports of the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India referred to in clause (2) of article 151 relating to the accounts of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir in respect of any period prior to the appointed day shall be submitted to the Lieutenant Governors of the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, and Union territory of Ladakh.
(2) The Lieutenant Governor of Jammu and Kashmir, thereafter shall cause the reports to be laid before the Legislature of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(3) The Lieutenant Governor of Jammu and Kashmir may by order-
(a) declare any expenditure incurred out of the Consolidated Fund of Jammu and Kashmir on any service in respect of any period prior to the appointed day during the financial year or in respect of any earlier financial year in excess of the amount granted for that service and for that year as disclosed in the reports referred to in sub-section (1) to have been duly authorised; and
(b) provide for any action to be taken on any matter arising out of the said reports.
83. Distribution of revenue.
(1) The award made by the Fourteenth Finance Commission to the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall be apportioned between the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir; and Union territory of Ladakh by the Central Government on the basis of population ratio and other parameters:
Provided that on the appointed day, the President shall make a reference to the Union territories Finance Commission to take into account the resources available to the successor Union territories of Ladakh and make separate award for the successor Union territory of Ladakh:
Provided further that on the appointed day, the President shall make a reference to the Fifteenth Finance Commission to include Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir in its Terms of Reference and make award for the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(2) Notwithstanding anything in sub-section (1), the Central Government may, having regard to the resources available to the successor Union territory of Ladakh make appropriate grants and also ensure that adequate benefits and incentives in the form of special development package are given to the backward areas of this region.
PART XI OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – APPORTIONMENT OF ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
84. Application of this Part.
(1) The provisions of this Part shall apply in relation to the apportionment of the assets and liabilities of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir immediately before the appointed day, between the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and successor Union territory of Ladakh.
(2) The apportionment of the assets and liabilities of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall be subject to the recommendations of a committee constituted by the Central Government.
(3) The process of apportionment shall be completed within a period of twelve months from the appointed day.
PART XII OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – PROVISIONS AS TO CERTAIN CORPORATIONS AND ANY OTHER MATTERS
85. Advisory Committee(s).
(1) The Central Government may by order, establish one or more Advisory Committees within a period of 90 days from the appointed day, for the purposes of:
(a) apportionment of assets, rights and liabilities of the companies and corporations constituted for the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir between Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh;
(b) issues relating to Continuance of arrangements in regard to generation and supply of electric power and supply of water;
(c) issues related to Jammu and Kashmir State Financial Corporation;
(d) issues related to Companies constituted for the existing state of Jammu and Kashmir
regarding the division of the interests and shares and reconstitution of Board of Directors; (e) issues related to facilities in certain State Institutions; and
(f) issues related to any other matters not covered under this section.
(2) The committees so appointed under sub-section (1) of this section, shall submit their reports within six months to the Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, who shall act on the recommendations of such committees within a period of 30 days from the date of receiving such reports.
86. Temporary provisions as to continuance of certain existing road transport permits.
(1) Notwithstanding anything contained in section 88 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 (59 of 1988), a permit granted by the State Transport Authority of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir or any Regional Transport Authority in that State shall, if such permit was, immediately before the appointed day, valid and effective in any area in the transferred territory, be deemed to continue to be valid and effective in that area after that day till its period of validity subject to the provisions of that Act as for the time being in force in that area; and it shall not be necessary for any such permit to be countersigned by the Transport Authority of any of Union territory or any Regional Transport Authority therein for the purpose of validating it for use in such area:
Provided that the Lieutenant Governor may add to amend or vary the conditions attached to the permit by the Authority by which the permit was granted.
(2) No tolls, entrance fees or other charges of a like nature shall be levied after the appointed day in respect of any transport vehicle for its operations in any of the successor Union territories under any such permit, if such vehicle was, immediately before that day, exempt from the payment of any such toll, entrance fees or other charges for its operations in the transferred territory:
Provided that the Central Government may, after consultation with the Government of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or the administration of Union territory of Ladakh, as the case may be, authorise the levy of any such toll, entrance fees or other charges, as the case may be:
Provided further that the provisions of this sub-section shall not be applicable where any such tolls, entrance fees or other charges of a like nature are leviable for the use of any road or bridge which is constructed or developed for commercial purpose by the State Government, an undertaking of the State Government, a joint undertaking in which the State Government is a shareholder or the private sector.
87. Special provision as to income-tax.
Where the assets, rights and liabilities of any body corporate carrying on business are, under the provisions of this Part, transferred to any other bodies corporate which after the transfer carry on the same business, the losses or profits or gains sustained by the body corporate first-mentioned which, but for such transfer, would have been allowed to be carried forward and set off in accordance with the provisions of Chapter VI of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (43 of 1961), shall be apportioned amongst the transferee bodies corporate in accordance with the rules to be made by the Central Government in this behalf and, upon such apportionment, the share of loss allotted to each transferee body corporate shall be dealt with in accordance with the provisions of Chapter VI of the said Act, as if the transferee body corporate had itself sustained such loss in a business carried on by it in the years in which those losses were sustained.
PART XIII OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – PROVISIONS AS TO SERVICES
88. Provisions relating to All India Services.
(1) In this section, the expression “State cadre” (a) in relation to the Indian Administrative Service, has the same meaning assigned to it in
the Indian Administrative Service (Cadre) Rules, 1954 [IAS (cadre) rules, 1954];
(b) in relation to the Indian Police Service, has the same meaning assigned to it in the Indian Police Service (Cadre) Rules, 1954 [IPS (cadre) rules, 1954]; and
(c) in relation to the Indian Forest Service, has the same meaning assigned to it in the Indian Forest Service (Cadre) Rules, 1966 [IFS (cadre) rules, 1954].
(2) The members of the cadres of Indian Administrative Service, Indian Police Service and Indian Forest Service for the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir, on and from the appointed day, shall continue to function on the existing cadres.
(3) The provisional strength, composition and allocation of officers currently borne on the existing cadre of Jammu and Kashmir to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh, as referred to in sub-section (2) shall be such as the Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir may, by order, determine on or after the appointed day.
(4) The members of each of the said services, currently borne on the Jammu and Kashmir cadre immediately before the appointed day shall be finally allocated between the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh, in such manner and with effect from such date or dates as the Central Government may, by order, specify on the recommendation of Lieutenant Governors of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir; and Union territory of Ladakh.
(5) The Officers so allocated to both the Union Territories shall function within these Union Territories, in accordance with the rules framed by the Central Government.
(6) In future, the All India Service officers to be posted to Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or Union territory of Ladakh, as the case may be, shall be borne on the Arunachal Goa Mizoram Union territory cadre, and necessary modifications in corresponding cadre allocations rules may be made accordingly, by the Central Government.
89. Provisions relating to other services.
(1) Every person who immediately before the appointed day is serving on substantive basis in connection with the affairs of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall, on and from that day provisionally continue to serve in connection with the affairs of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh, by general or special order of the Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir:
Provided that every direction under this sub-section issued after the expiry of a period of one year from the appointed day shall be issued with the consultation of the Government or Administration of the successor Union territories, as the case may be.
(2) As soon as may be after the appointed day, the Lieutenant Governor of Jammu and Kashmir shall, by general or special order, determine the successor Union territory to which every person referred to in sub-section (1) shall be finally allotted for service, after consideration of option received by seeking option from the employees, and the date with effect from which such allotment shall take effect or be deemed to have taken effect:
Provided that even after the allocation has been made, Lieutenant Governor of Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir may in order to meet any deficiency in the service, depute officers from one successor Union territory to the other Union territory.
(3) Every person who is finally allotted under the provisions of sub-section (2) to a successor Union territory shall, if he is not already serving therein, be made available for serving in the successor Union territory from such date as may be agreed upon between the Government of the successor Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Administration of Union territory of Ladakh, or, in default of such agreement, as may be determined by the Central Government:
Provided that the Central Government shall have the power to review any of its orders issued under this section.
90. Other provisions relating to services.
(1) Nothing in this section or in section 89 shall be deemed to affect, on or after the appointed day, the operation of the provisions of Chapter I of Part XIV of the Constitution in relation to determination of the conditions of service of persons serving in connection with the affairs of the Union or any Union territory:
Provided that the conditions of service applicable immediately before the appointed day in the case of any person deemed to have been allocated to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or Union territory of Ladakh under section 89 shall not be varied to his disadvantage except with the previous approval of the Lieutenant Governor.
(2) All services prior to the appointed day rendered by a person,-
(a) if he is deemed to have been allocated to any Union territory under section 89, shall be
deemed to have been rendered in connection with the affairs of that Union territory;
(b) if he is deemed to have been allocated to the Union in connection with the administration of the successor Union territory, shall be deemed to have been rendered in connection with the affairs of the Union, for the purposes of the rules regulating his conditions of service.
(3) The provisions of section 89 shall not apply in relation to members of any All-India Service.
91. Provisions as to continuance of officers in same post.
Every person who, immediately before the appointed day, is holding or discharging the duties of any post or office in connection with the affairs of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir in any area which on that day falls within one of the successor Union territory shall continue to hold the same post or office in that successor Union territory, and shall be deemed, on and from that day, to have been duly appointed to the post or office by the Government of, or other appropriate authority in, that successor Union territory:
Provided that nothing in this section shall be deemed to prevent a competent authority, on and from the appointed day, from passing in relation to such person any order affecting the continuance in such post or office.
92. Provision for employees of Public Sector Undertakings, etc.
On and from the appointed day, the employees of State Public Sector Undertakings, corporations and other autonomous bodies shall continue to function in such undertaking, corporation or autonomous bodies for a period of one year and during this period the corporate body concerned shall determine the modalities for distributing the personnel between the successor Union territories.
93. Provisions as to State Public Service Commission.
(1) The Public Service Commission for the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall, on and from the appointed day, be the Public Service Commission for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(2) The Union Public Service Commission, with the approval of the President, shall serve the needs of the Union territory of Ladakh.
(3) The persons holding office immediately before the appointed day as the Chairman or other member of the Public Service Commission for the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall, as from the appointed day, be the Chairman or, as the case may be, the other member of the Public Service Commission for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
(4) Every person who becomes the Chairman or other member of the Public Service Commission for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir on the appointed day under sub-section (3) shall be entitled to receive from the Government of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, conditions of service not less favourable than those to which he was entitled under the provisions applicable to him.
(5) The report of the Jammu and Kashmir Public Service Commission as to the work done by the Commission in respect of any period prior to the appointed day shall be presented to the Lieutenant Governor of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, and the Lieutenant Governor of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir shall, on receipt of such report, cause a copy thereof together with a memorandum explaining as far as possible, as respects the cases, if any, where the advice of the Commission was not accepted, the reasons for such non-acceptance to be laid before the Legislature of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
PART XIV OF THE JAMMU AND KASHMIR REORGANISATION ACT, 2019 – LEGAL AND MISCELLANEOUS PROVISIONS
94. Amendment of section 15 of Act 37 of 1956.
On and from the appointed day, in section 15 of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, in clause (a), for the words “Jammu and Kashmir” the words “Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh” shall be substituted.
95. Territorial extent of laws.
(1) All Central laws in Table-1 of the Fifth Schedule to this Act, on and from the appointed day, shall apply in the manner as provided therein, to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh.
(2) All other laws in Fifth Schedule, applicable to existing State of Jammu and Kashmir immediately before the appointed day, shall apply in the manner as provided therein, to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and Union territory of Ladakh.
96. Power to adapt laws.
For the purpose of facilitating the application in relation to the successor Union territories, of any law made before the appointed day, as detailed in Fifth Schedule to this Act, the Central Government may, before the expiration of one year from that day, by order, make such adaptations and modifications of the law, whether by way of repeal or amendment, as may be necessary or expedient, and thereupon every such law shall have effect subject to the adaptations and modifications so made until altered, repealed or amended by a competent Legislature or other competent authority.
97. Power to construe laws.
Notwithstanding that no provision or insufficient provision has been made under section 96 for the adaptation of a law made before the appointed day, any court, tribunal or authority, required or empowered to enforce such law may, for the purpose of facilitating its application in relation to the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or Union territory of Ladakh, construe the law in such manner, without affecting the substance, as may be necessary or proper in regard to the matter before the court, tribunal or authority.
98. Power to name authorities, etc., for exercising statutory functions.
The Lieutenant Governor, as respects the concerned territory may, by notification in the Official Gazette, specify the authority, officer or person who, on or after the appointed day, shall be competent to exercise such functions exercisable under any law in force on that day as may be mentioned in that notification and such law shall have effect accordingly.
99. Legal proceedings.
Where, immediately before the appointed day, the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir is a party to any legal proceedings with respect to any property, rights or liabilities subject to apportionment among the successor Union territories under this Act, the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir or the Union territory of Ladakh which succeeds to, or acquires a share in, that property or those rights or liabilities by virtue of any provision of this Act shall be deemed to be substituted for the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir or added as a party to those proceedings, and the proceedings may continue accordingly.
100. Transfer of pending proceedings.
(1) Every proceeding pending immediately before the appointed day before a court (other than High Court), tribunal, authority or officer in any area which on that day falls within the State of Jammu and Kashmir shall, if it is a proceeding relating exclusively to the territory, which as from that day are the territories of any Union territory, stand transferred to the corresponding court, tribunal, authority or officer of that Union territory.
(2) If any question arises as to whether any proceeding should stand transferred under sub-section (1), it shall be referred to the common High Court of Jammu and Kashmir and the decision of that High Court shall be final.
(3) In this section-
(a) proceeding includes any suit, case or appeal; and
(b) corresponding court, tribunal authority or officer in any of Union territory means-
(i) the court, tribunal, authority or officer in which, or before whom, the proceeding would have laid if it had been instituted after the appointed day; or
(ii) in case of doubt, such court, tribunal, authority, or officer in that Union territory, as may be determined after the appointed day by the Government or administration of that Union territory, or the Central Government, as the case may be, or before the appointed day by the Government of the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir to be the corresponding court, tribunal, authority or officer.
101. Right of pleaders to practise in certain cases.
Any person who, immediately before the appointed day, is enrolled as a pleader entitled to practise in any subordinate court in the existing State of Jammu and Kashmir shall, for a period of one year from that day, continue to be entitled to practise in those courts, notwithstanding that the whole or any part of the territories within the jurisdiction of those courts has been transferred to any of the Union territories.
102. Effect of provisions of the Act inconsistent with other laws.
The provisions of this Act shall have effect notwithstanding anything inconsistent therewith contained in any other law.
103. Power to remove difficulties.
(1) If any difficulty arises in giving effect to the provisions of this Act, the President may, by order do anything not inconsistent with such provisions which appears to him to be necessary or expedient for the purpose of removing the difficulty:
Provided that no such order shall be made after the expiry of a period of five years from the appointed day.
(2) Every order made under this section shall be laid before each House of Parliament.
For the Schedule and rest of the options please go here and download the official PDF
Get the PDF for Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization Act, 2019
- Article 334A of the Constitution of India - 14th April 2024
- Article 332A of the Constitution of India - 14th April 2024
- Article 330A of the Constitution of India - 14th April 2024







